The Ultimate Guide to Generating Income With Options
If you want to start trading options, I created the ultimate guide to generating income with options in this post.
You can also learn about technical analysis for options trading to improve your trade timing.
Options Trading Terminology
Before you learn how options work, you must know all the basic options trading terminology. If you don’t understand the terminology, you will struggle to grasp how to make income trading options.
- Strike price (exercise price)
The strike price of an option is the price at which both parties agree to buy or sell the underlying stock.
- Premium
The premium of an options contract is the price you can buy or sell the contract.
- ITM (in the money)
An ITM option refers to a contract that contains intrinsic value. In other words, it is favorable for the buyer to exercise.
- OTM (out of the money)
An option contract is OTM when it does not have any intrinsic value and is unfavorable for the contract owner to exercise.
- Expiration date
The expiration date of an option is the last date on which the buyer can exercise the right to buy or sell the underlying stock.
- Buy to open vs. buy to close
When you buy to open an option, you are opening a long position on the contract. Buying to close an option means closing a position you initially shorted by selling it to open.
- What is a Call Option?
A call option gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the strike price.
- What is a Put Option?
A put option gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the strike price.
Selling vs. Buying Options
Options traders can choose to buy or sell options contracts. The buyer of an options contract pays a premium for the right to buy or sell shares of the underlying stock. Option buyers are usually speculating on the direction a stock will move.
The seller of an options contract receives a premium in exchange for taking on the obligation to buy or sell shares of the underlying stock. Option sellers generally seek to generate income for their portfolio by collecting premiums from the option buyers.
The Best Options Income Trading Strategies
Now that you understand the basics of options, we will introduce some of the various options trading strategies you can employ.
- Cash Secured Puts
A cash-secured put is when you promise to buy 100 shares of stock by selling to open a put contract. You will get paid a premium in exchange for taking on the obligation to purchase 100 shares.
- Covered Calls
The covered call options strategy is when you purchase 100 shares of a stock and then sell a call option against them. Essentially, you are getting paid for promising to sell your shares at the strike price.
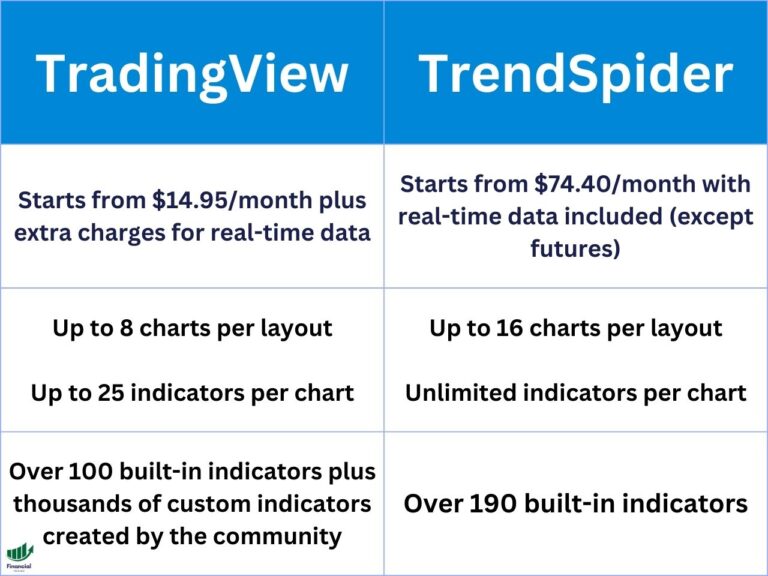
- Credit Spreads
A call credit spread is when you sell a call option, then delta hedge it by purchasing a higher strike call option within the same expiration date. Call credit spreads are also known as bear call spreads.
A put credit spread is when you sell a put option, then delta hedge it by purchasing a lower strike put option within the same expiration date. Put credit spreads are also known as bull put spreads.
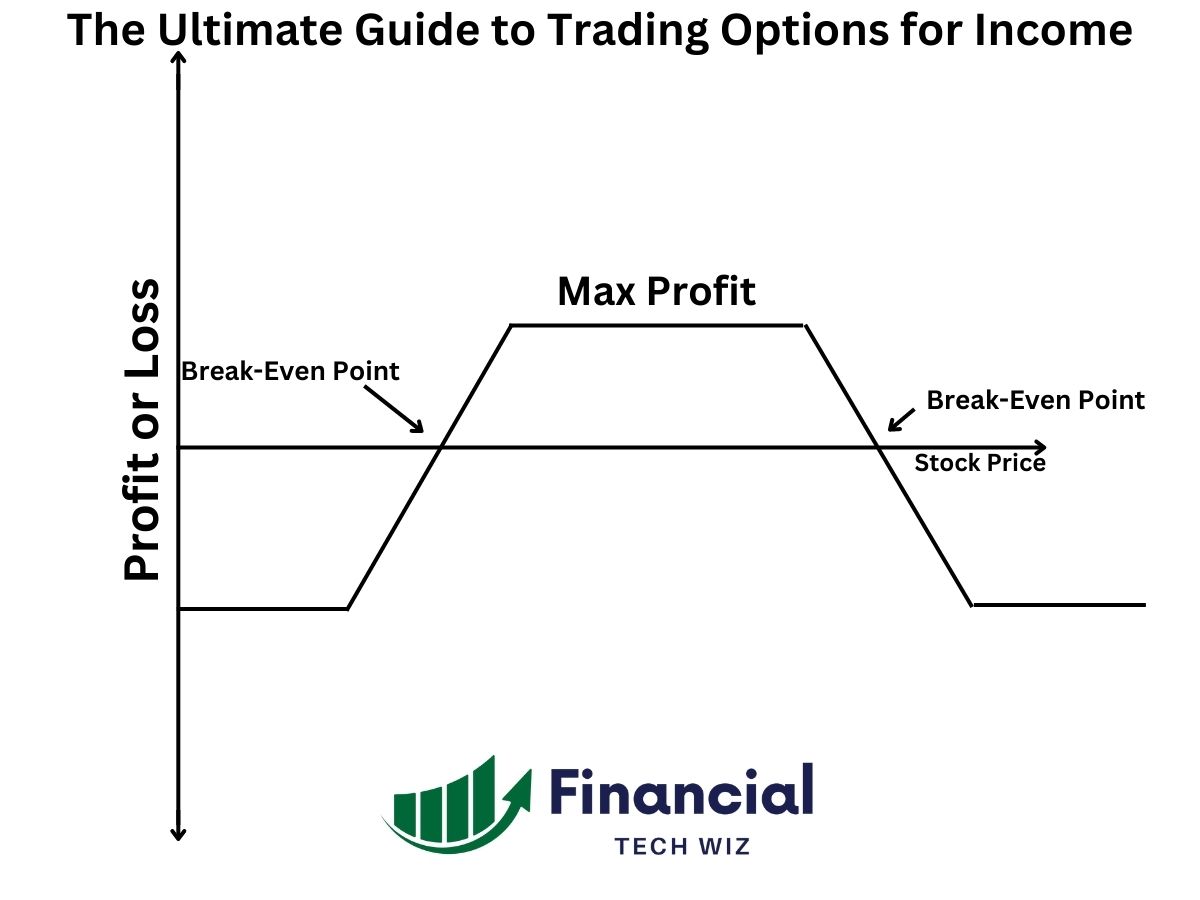
The iron condor options strategy is when you combine a put credit spread and a call credit spread. Therefore, it is a delta-neutral options strategy where you want the underlying stock price to stay in between the two credit spreads.
- Short Strangle
The short strangle options strategy is when you sell a call and a put within the same expiration date. The short strangle is an iron condor without the long options to delta hedge, meaning the short strangle is a naked strategy.
- Short Straddle
The short straddle is when you sell a call and a put option with the same strike price. It is the same as a short strangle, except the strikes must be the same and usually placed at the current stock price.
The jade lizard options strategy is when you sell a naked put option and a bear call spread within the same expiration date. The jade lizard is a short strangle, except the call side is a call credit spread, not a naked call. Tastytrade commonly uses this strategy to prevent upside risk.
- Poor Man’s Covered Call
The poor man’s covered call is an options strategy that involves purchasing a deep ITM call option and then selling a shorter-term call against that call.
- The Wheel Strategy
The wheel strategy starts by selling cash-secured puts until you are assigned 100 shares of stock. Once you own 100 shares, you sell covered calls until you get called away, completing the wheel strategy.
- Short Put
A short put is the same as a cash-secured put, except you don’t set aside money to buy 100 shares at the strike price. Instead, you utilize margin to collect premium selling puts.
Rolling Options
Rolling an option is when you close your current position and simultaneously open a new one. Options traders roll their positions when they want to manage risk, extend their expiration date, or collect more premiums.
Rolling options forward means moving the position to a further expiration date. Rolling an option up or down means you are changing the strike price. You can also roll an option forward and up or down.
Implied Volatility Rank
The implied volatility of a security is a metric that determines how much the market believes the security will move. In other words, high implied volatility (IV) means that the market believes the security will move significantly. For example, the IV of a stock will rise around events such as earnings since investors believe the results will dramatically affect the stock price.
The IV rank of a security is a measure of the current implied volatility compared to the last 52 weeks. IV is based on a scale of 0-100, where 0 is the lowest IV print, and 100 is the highest IV print over the last 52 weeks.
The stock’s IV percentile is another metric that compares a security’s current IV with its last 52 weeks of trading. The difference is that the IV percentile states the percentage of days over the previous 52 weeks that IV traded below its current implied volatility.
Options Greek Cheat Sheet
The options greeks are crucial to know for options traders because they give you insight into how an option contract will react to changes in volatility, stock price, time, and more.
- Delta
An options delta has two meanings. The first meaning of an options delta is the probability that it will expire ITM. The other meaning of delta is the amount an option will change for every $1 increase in the underlying stock price.
- Theta
The theta of an option is the amount an option will decrease for every day that passes.
- Vega
The vega of an option is the amount an option will change for every one-point change in implied volatility.
- Gamma
Option gamma is the second order greek to the delta. It measures the rate of delta change for every one point move in the underlying stock.
- Vomma
Vomma is the second-order greek to vega. It measures the amount vega will change based on implied volatility changes.
- Color
Color is a third-order greek that measures the rate at which gamma will change over time.
- Charm
Charm is a second-order greek that measures the amount an options delta will decay over time.
- Rho
Rho is the amount an option will change based on a one-point move in interest rates.
Evaluating Your Risk Tolerance
Before you start trading options, you must determine your risk tolerance. Then, depending on your trading experience, you may want to start with smaller trades so you do not get emotional after placing a trade.
If you are brand new to options trading, you should start small until you experience a bad trade. It is impossible to replicate how it feels to lose your hard-earned money without actually losing it on an options trade.
Risk/Reward of Options Strategies
There are many different options strategies, and they all come with different risk profiles.
Buying a call
Buying a call option is an easy trade to understand because the max risk is the price you pay for the contract. However, you must realize that call options expire, and if the stock doesn’t move above your strike price before it expires, you will lose all your money.
The most popular call buying strategy is buying LEAPs (long-term anticipation security). A LEAPs call is a call option with over a year until expiration. LEAPs are an excellent call buying strategy because you have a long time until expiration, and it is similar to holding stock shares for much cheaper.
Buying a put
The maximum loss when buying a put is the price you pay for the contract, just like buying a call. Traders may buy puts to hedge their long stock portfolios, speculate on the stock market’s decline, or want to go long volatility.
Buying a put is an excellent way to short a stock without using margin. However, you must deal with picking the correct expiration date.
Writing a put
The maximum risk you face when writing a put option is being assigned 100 shares of the underlying stock at the puts strike price. Many traders, even Warren Buffett, sell put options to generate income and purchase a stock since the reward is collecting the option premium.
If you have a margin account, you may be able to sell a lot more put options than your account can handle. Therefore, you must understand the risks you are taking, and if you are unsure, only trade cash-secured puts.
Writing a call
Writing a call is the riskiest options strategy because your max risk is theoretically unlimited. For example, the max risk of selling a naked call option is you end up short 100 shares of the stock at the strike price.
Stock prices can continue up indefinitely. Therefore, short sellers have unlimited risk. However, if you own 100 shares of stock and sell a call, that is a much safer strategy called the covered call.
Reasons to Trade Options
The primary use of options trading is to hedge risk. For example, investors can buy put options to limit the downside risk on their stocks.
Traders can also buy call options to hedge a short position. Since short positions have unlimited risk, you can cap the exposure with call options.
How do Call Options Make Money?
Call options make money when you buy them, and the stock moves up shortly after. However, there are other factors working against you, such as theta or time decay.
For example, if you buy an OTM call option and the stock stays flat for the next three months, you will lose money because expiration is getting closer.
The safest way to buy call options is to purchase long-term ITM call options. This strategy is the safest because ITM call options have intrinsic value and are less affected by theta decay.
Selecting the Right Options to Trade
Selecting the best options to trade is based on a few factors. Most importantly, you must know if you are bearish or bullish on the underlying stock.
You can buy a call option or write a put if you are bullish.
If you are bearish on a stock, you can buy a put or write a call.
The next question is whether selling or buying an option is better. If implied volatility is high, it is generally better to sell options and vice versa.
For example, if you believe a stock is overvalued and the implied volatility is elevated, it would be better to sell a call than buy a put.
Can I Sell Options Immediately?
Yes, you can sell your option anytime you want after buying it. Depending on the goals of the trade, you can hold it until expiration or sell it early.
However, the stock market must be open for you to buy and sell options. When it is closed, you are not able to trade actively.
Options Trading Tips
Deciding which options to trade can be confusing if you don’t have a strategy outlined. To increase your trading confidence, you should primarily determine whether you want to sell or buy options.
Option sellers have a high win rate but then have big losers.
Options buyers lose a lot but occasionally have a big winner.
You can see significant losses if you do not manage your risk as an option seller. Many traders that sell options spend some of the collected premium on purchasing options to hedge their short options trades, forming a spread.
Regardless of your chosen strategy, your main goal is to manage risk. Options trading is risky, and you can blow up your account if you do not understand your risk tolerance.
The Ultimate Guide to Generating Income With Options
Regardless of your position in the stock market, you can utilize various options strategies to generate income or hedge your portfolio. Even investors like Warren Buffet use options strategies like the cash-secured put to purchase shares of stock at a discount.
However, options trading is not suitable for everybody with the risks involved. Therefore, before starting options trading, you must figure out how to create a profitable trading system. If you blindly go into the options market, you have a low chance of being profitable.
This article contains affiliate links I may be compensated for if you click them.
– Free trading journal template & cheat sheet PDFs
– Access our custom scanners and watchlists
– Access our free trading course and community!