What is a Fair Value Gap (FVG) in Trading?
This article will show you how to identify, trade, and understand the fair value gap in trading.
Fair Value Gaps Meaning Explained for Traders
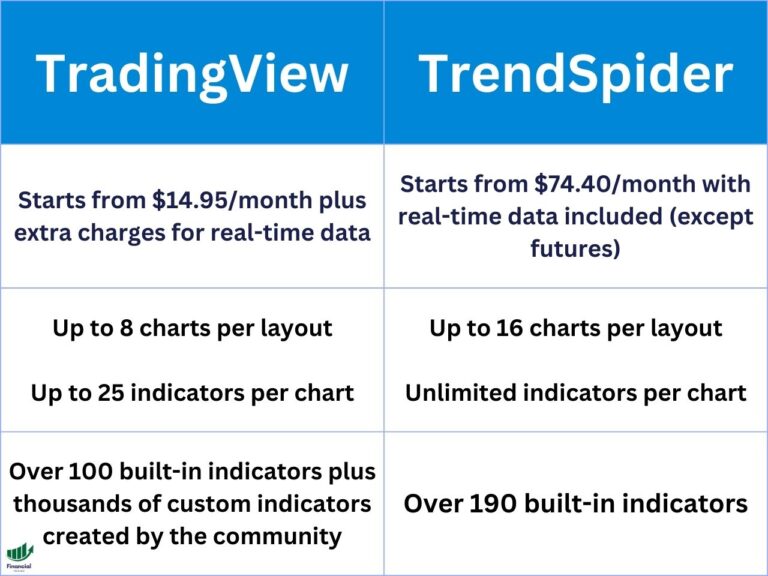
A fair value gap (FVG) in trading is a three-candlestick pattern that is created by imbalances between buyers and sellers.
Like a regular gap, the fair value gap acts as a magnet, drawing the asset’s price to eventually fill the gap and repair the imbalance in the market.
An FVG can occur on any timeframe, from the 1-minute chart to the daily chart.
Join for FREE: Access tons of free educational material!
Don’t miss out – Join now and start learning!
- Free Educational Material
- Community for Like-Minded Traders
- Personalized Trading Education
How to Identify a Fair Value Gap
Identifying fair value gaps can be a difficult task, so let’s break it down step by step:
1- Find a Large Imbalance Candle
The first step to identifying a fair value gap is to find an abnormally large candle that causes a clear imbalance between buyers and sellers. Large candles can be caused by news, economic events, or volatile price action. The large candle can be either red or green.
2- Identify the Fair Value Gap on the Chart
Once you identify the large candle, you must analyze the candles directly to the left and right. The highs and lows of these candles determine the fair value gap range, which we can draw on our TradingView charts with horizontal lines or a rectangle.
If the large candle is green, the fair value gap is defined as the area of the preceding candle’s high and the following candle’s low. Note that the neighboring candles should not significantly overlap the large candle, as in this case, there wouldn’t be much of a gap.
Fair Value Gap Indicator
One of the best fair value gap indicators around is the LuxAlgo HTF Fair Value Gap on TradingView.
If you want to try this indicator out for free, you can sign up with our TradingView affiliate link to receive a 30-day free trial and a discount on your subscription.
Exclusive Deal: 30-Day FREE Premium Access + Bonus Credit
Don’t Miss Out – Sign up for TradingView Now!
- Advanced Fair Value Gap Tools
- Real-Time Market Data
- Track All Market Trends
Bullish vs. Bearish Fair Value Gaps
Fair value gaps can either be bullish or bearish, depending on the overall trend and color of the candles.
Bullish Fair Value Gaps
A bullish fair value gap is identified by a large green candle and states that an asset price recently increased too quickly and may be temporarily overvalued. Therefore, it is likely that the price will eventually come down and fill the fair value gap before continuing higher.
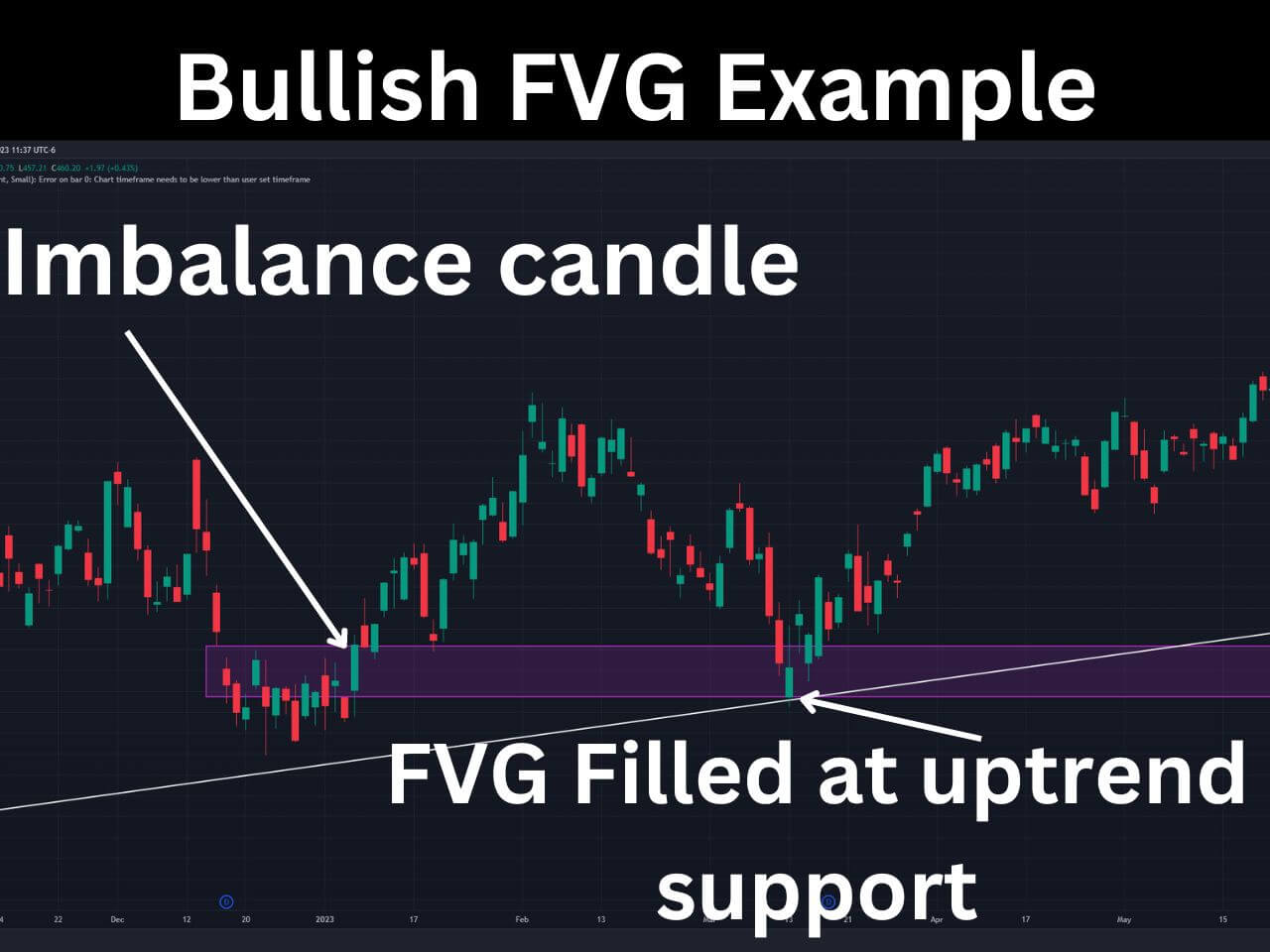
Bullish Fair Value Gap Example
An excellent example of a bullish FVG can be found on the SPY daily chart on 1/6/2023. Price was steadily consolidating, then a large green candlestick created an FVG, identified by the rectangle on the chart. The bullish FVG is determined by the preceding candles’ high and the following candles’ low.
Bearish Fair Value Gaps
A bearish fair value gap is identified by a large red candle and means that the asset price is temporarily undervalued. Eventually, traders will likely see the price repair this imbalance by increasing and filling the fair value gap. The bearish FVG is determined by the preceding candles’ low and the following candles’ high.
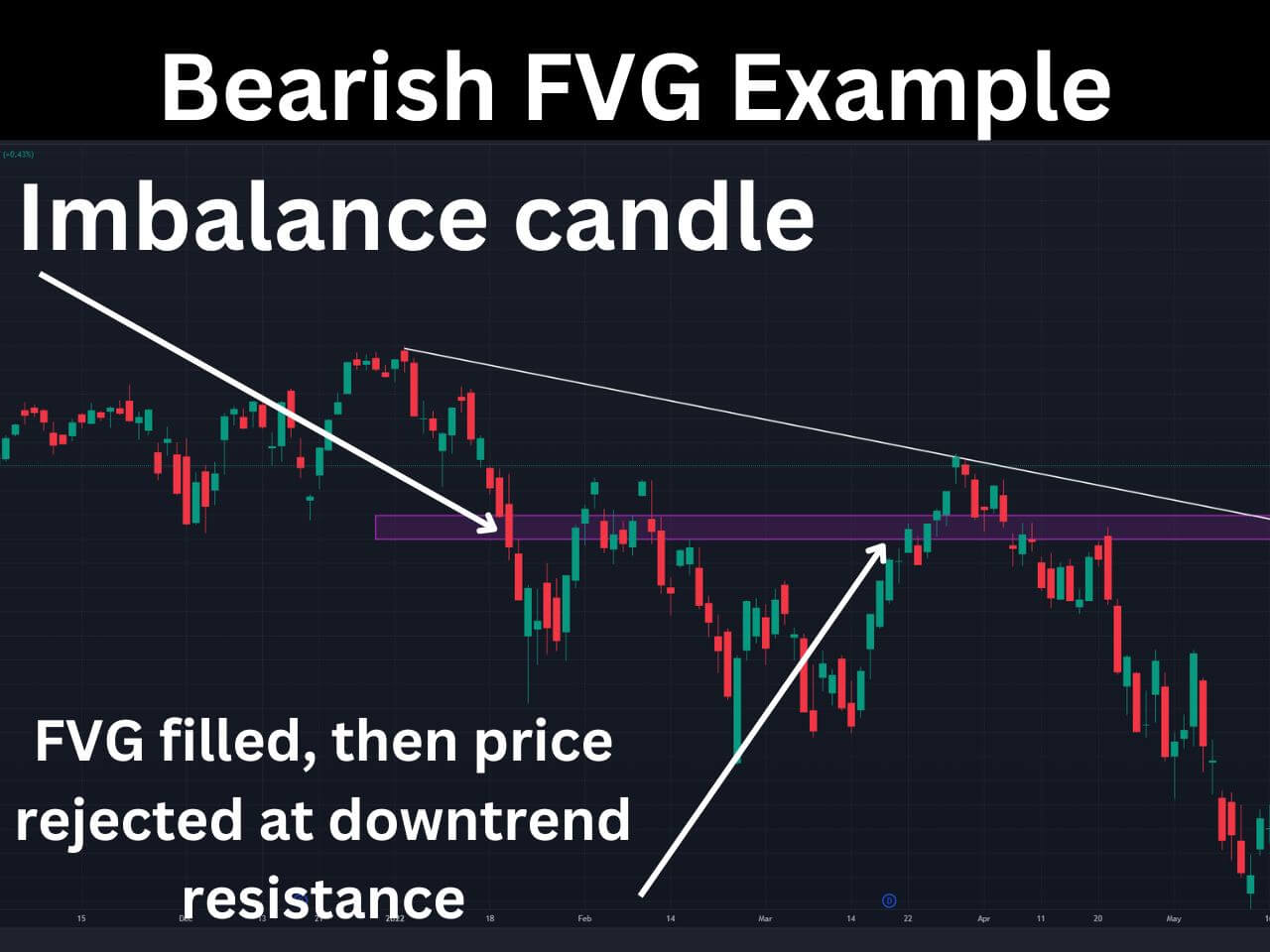
Bearish Fair Value Gap Example
An example of a bearish fair value gap lies on the SPY daily chart on 1/20/2022. The FVG is marked by the purple rectangle, and we also determined the overall trend was down based on the trendline.
Identifying the Overall Trend
The overall trend of an asset is crucial when determining how you will trade the fair value gap. For example, if a stock is in an overall downtrend and you notice a bearish fair value gap, traders will consider shorting when the price fills the FVG. Ideally, the FVG is near a resistance level determined by another indicator or a bearish trendline.
FVG Trading Strategy – Trading Fair Value Gaps
Now that you understand what a fair value gap is and how to identify one let’s cover a basic FVG trading strategy you can try.
1- Identify a Fair Value Gap
Say for example, you identified the bullish fair value gap we used as an example above on the SPY daily chart. You would draw on your TradingView chart to mark the FVG and proceed to wait for an entry point.
2- Identify the Trend
In our bullish example, we determined that the trend was bullish, identified by our upward trendline.
3- Determine Entry and Exit Points
To determine an entry point on this bullish fair value gap, you must wait for the gap to fill and proceed to go long once it does. The gap perfectly aligns with our upward trendline, giving it a higher chance to play out.
4- Risk Management When Using Fair Value Gaps
Nothing is guaranteed in the world of trading, so it would be wise to set a stop loss below the trendline and FVG, in case the strategy doesn’t play out like expected to limit your loss potential.
5- When to Take Profit Using a FVG Strategy
When trading a bullish FVG setup, you can take profit when the asset increases to the next level of resistance or demand zone. Setting a sell order is great, but sometimes, you can miss out on bigger moves.
Alternatively, you can set a stop loss in profit below a support level. You will avoid selling too early by waiting for the asset to break support. However, you may generate less profit than if you attempted to sell at the ‘top’ using resistance levels.
Related Articles
How to Get Candlesticks on TradingView
– Free trading journal template & cheat sheet PDFs
– Access our custom scanners and watchlists
– Access our free trading course and community!