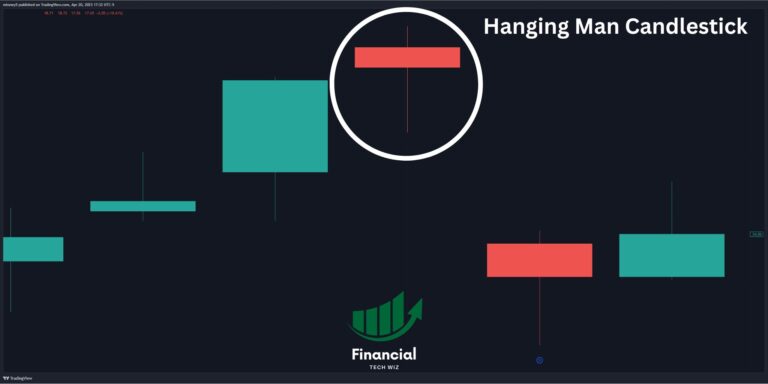
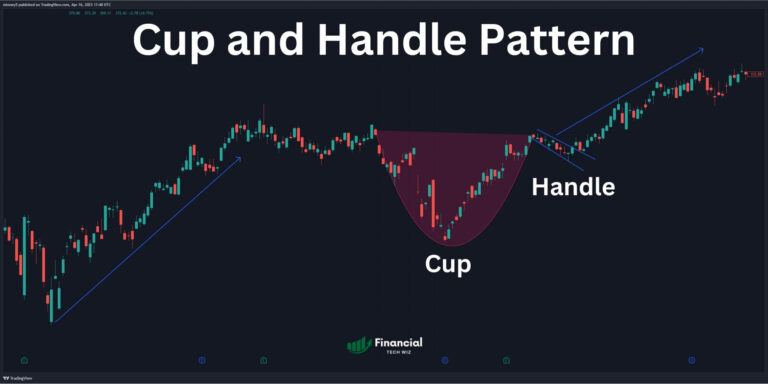
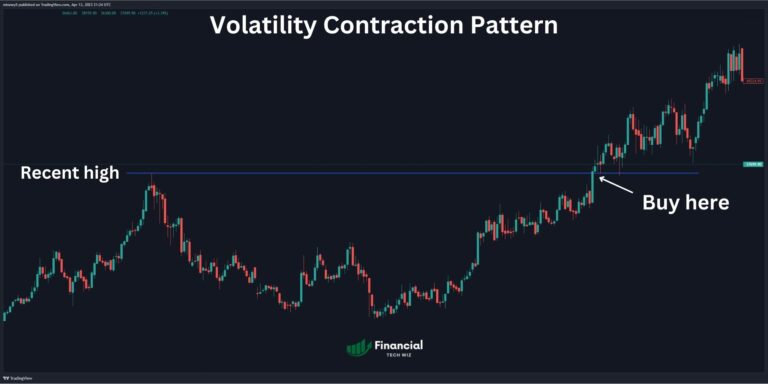
Hanging Man Candle: Recognizing Bearish Reversals
Candlestick patterns play a crucial role in technical analysis, offering valuable insights to traders and investors. Among these patterns, the Hanging Man candlestick pattern stands out as a noteworthy signal, often indicating a potential bearish reversal. This guide will explore the nuances of the Hanging Man pattern, compare it with similar patterns, and provide practical…