Bear Trap Stock Pattern: A Comprehensive Guide for Traders
The financial market is dynamic and ever-changing, where traders and investors continuously seek opportunities to maximize profits. In this pursuit, market participants must be aware of certain technical patterns that could lead to unexpected outcomes.
One such pattern is the bear trap—an event that can catch even seasoned traders off guard. In this guide, we’ll delve into the mechanics of bear traps, explore how to identify and avoid them, and offer valuable insights for informed trading decisions.
What is a Bear Trap on the Stock Market?
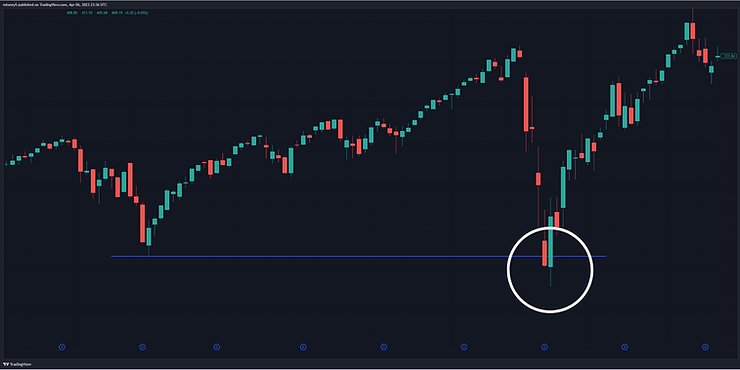
The bear trap stock pattern is a deceptive technical formation in which a financial asset’s price experiences a sudden and sharp decline, giving the impression that it’s entering a downtrend. However, this drop is short-lived and quickly followed by a strong reversal, causing the price to climb higher.
The term “bear trap” originates from the notion that bearish traders, who anticipate falling prices, are “trapped” by this false signal. As a result, traders who enter short positions during the decline incur losses when the price rebounds.
Exploring the Inner Workings
Bear traps occur in several stages:
- Initial Decline: The price of the asset undergoes a sudden drop, breaking below a key support level.
- Short Selling: Bearish traders interpret the decline as a bearish signal and enter short positions, hoping to profit from further price decreases.
- Reversal: Contrary to expectations, the price reverses direction and starts to rise sharply.
- Losses for Short Sellers: Short sellers are forced to cover their positions by buying back the asset at higher prices, resulting in losses.
Decoding the Causes
Bear traps can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Market News: Unexpected news or events that create uncertainty or fear in the market.
- Technical Factors: False bearish signals generated by technical analysis tools or chart patterns.
- Emotional Trading: Panic selling driven by fear and herd mentality among market participants.
Distinguishing Bear Traps from Bull Traps
While bear traps involve false signals of a downtrend followed by a price reversal upward, their counterparts—bull traps—operate in the opposite direction. Bull traps occur when a financial asset’s price breaks above a key resistance level, luring bullish traders into long positions. However, the upward movement is temporary, and the price reverses downward, causing losses for long-position traders.
Steering Clear of the Trap: Tips and Strategies
To avoid falling into bear traps, traders can consider the following approaches:
- Technical Analysis: Use technical indicators to assess support and resistance levels, trading volume, and overall market trends.
- Risk Management: Implement stop-loss orders to limit potential losses if the price moves against the anticipated direction.
- Alternative Strategies: Consider using put options as an alternative to short selling, as they provide a way to profit from price declines with limited risk.
- Patience: Exercise caution and avoid impulsive decisions based on short-term price movements.
Learning from Experience: A Practical Example
Consider a scenario where traders observe a stock trading at $100 with a key support level at $90. The stock’s price suddenly drops to $85, prompting bearish traders to enter short positions.
However, the decline is short-lived, and the price rebounds to $105, leaving the short sellers with losses. This exemplifies a classic bear trap, where traders acting on false signals incur financial setbacks.
Final Thoughts on Bear Traps
Bear traps are common in the financial market and can pose significant challenges for traders. By understanding the nature of bear traps, utilizing sound strategies, and keeping emotions in check, traders can navigate the market landscape with confidence and poise.
Being well-informed about deceptive market patterns, including bear traps, empowers traders to make informed decisions and avoid pitfalls on their journey to financial success. In the ever-changing and often unpredictable world of trading, knowledge is an invaluable asset that can lead to greater opportunities and rewards.
This article contains affiliate links I may be compensated for if you click them.
– Free trading journal template & cheat sheet PDFs
– Access our custom scanners and watchlists
– Access our free trading course and community!