Auction Market Theory: A Comprehensive Guide
Auction Market Theory (AMT) is a philosophy that offers traders and market participants a unique perspective on the movements of financial markets.
At its core, AMT focuses on the continuous interactions between buyers and sellers, the imbalances that arise, and the subsequent price discovery that occurs in the quest for fair value.
In this guide, we’ll dive into the key concepts of AMT and explore how it can enhance trading decision-making.
Auction Market Theory Explained
At the heart of AMT lies the concept of imbalances between buyer and seller aggression. These imbalances arise due to various market events that influence participants’ actions. As a result, the market experiences fluctuations in price levels as it seeks an equilibrium point.
- Fair Value: Central to AMT is the notion of “Fair Value,” the price area where trade is facilitated most efficiently. Here, buyer and seller aggression are closely balanced, resulting in stable trading within a relatively tight price range.
- Imbalanced Markets: Imbalances occur when market events prompt either buyers or sellers to dominate the trading landscape. When markets are imbalanced, prices move directionally, and the market enters a discovery phase in search of new value areas.
- Balanced Markets: Balanced markets represent a state of equilibrium where prices fluctuate near fair value. In this state, the aggression of buyers and sellers is harmonious, leading to steady trade volume.
Join for FREE: Access tons of free educational material!
Don’t miss out – Join now and start learning!
- Free Educational Material
- Community for Like-Minded Traders
- Personalized Trading Education
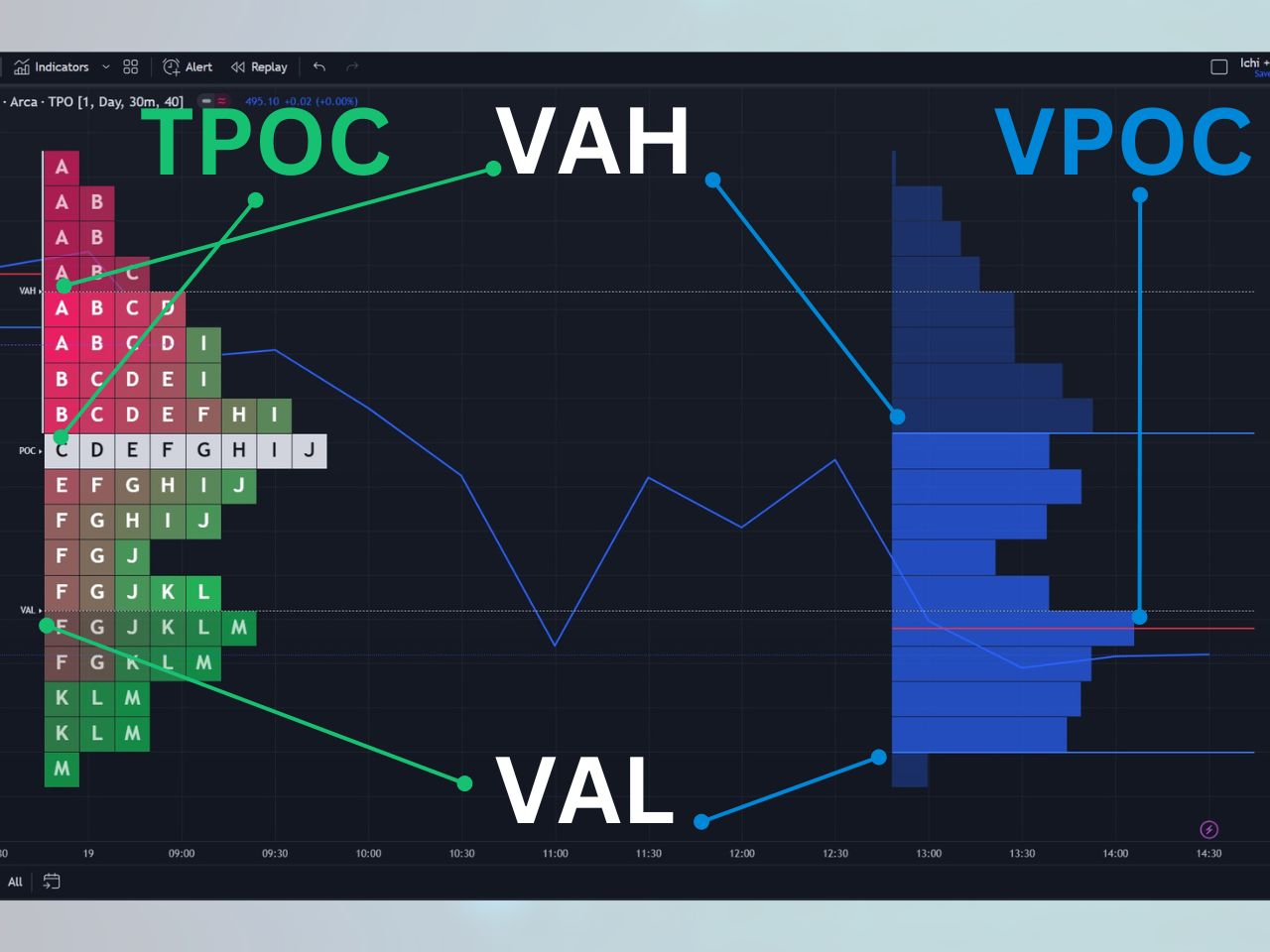
Market Profile: Visualizing Market Auctions
To better understand and analyze market auctions, traders often turn to a powerful charting tool known as Market Profile. Developed by Peter Steidlmayer in the early 1980s, Market Profile plots price distribution over time, offering valuable insights into market dynamics.
Market Profile is based on the concept of Time-Price Opportunity (TPO) and comprises three fundamental components: Price, Time, and Volume. The result is a visual representation of the market’s auction process, revealing patterns of herd behavior and the ebb and flow of price over time.
Key Applications of AMT in Trading
Armed with an understanding of AMT, traders can better navigate the financial markets and make informed trading decisions. Here are some practical applications:
- Mean Reversion in Balanced Markets: In balanced markets, AMT traders may look to fade moves away from Fair Value. This mean reversion strategy capitalizes on the market’s tendency to revert to a stable price point.
- Trend Trading in Imbalanced Markets: When markets are imbalanced, AMT traders may trade in the direction of the imbalance, capturing the market’s directional momentum during the discovery phase.
- Analyzing Order Flow and Volume: Traders can use Volume Profile alongside AMT to examine the distribution of trading volume at different price levels. This analysis offers insights into market participants’ actions and potential support and resistance zones.
The Potential of Auction Market Theory
Ultimately, AMT provides traders with a framework to interpret market dynamics, recognize patterns, and make strategic trading decisions. By incorporating AMT into their analysis, traders gain the ability to react to the ever-changing market landscape rather than merely attempting to predict it.
Whether you’re a seasoned trader or new to the financial markets, understanding Auction Market Theory can be a valuable addition to your trading arsenal. With AMT as your guide, you can confidently navigate the market’s constant shifts and unlock a world of trading opportunities.
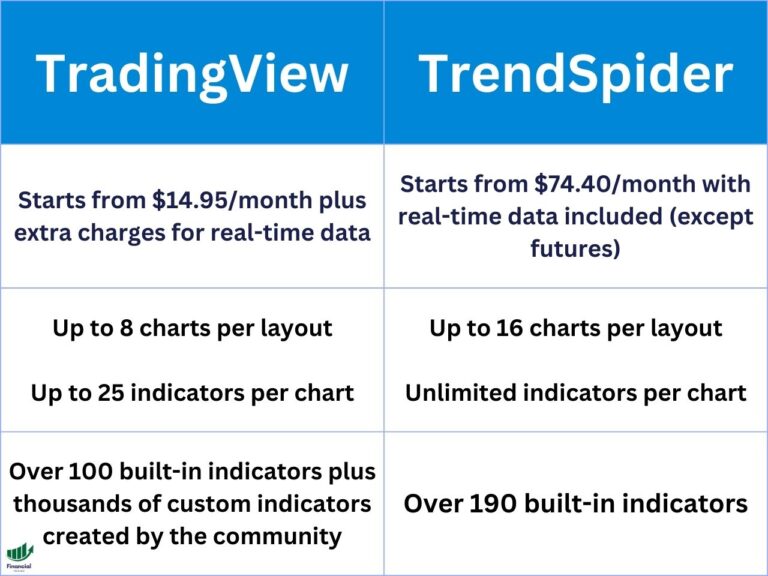
Leveraging Market Profile and Volume Profile on TradingView
For traders seeking to harness the power of Auction Market Theory, TradingView offers robust tools for visualizing and analyzing market auctions—Market Profile and Volume Profile. These tools allow traders to delve into the distribution of prices and trading volume, providing a deeper understanding of market dynamics.
Market Profile is a charting tool that plots the distribution of prices over time, offering insights into the two-way auction process. Through Market Profile, traders can identify areas of value, high-volume zones, and the ebb and flow of price, enhancing their decision-making process.
On the other hand, Volume Profile focuses on analyzing the distribution of trading volume at different price levels. By analyzing volume distribution, traders can uncover key support and resistance zones, gauge the actions of big buyers and sellers, and assess the strength of market trends.
TradingView offers a custom Market Profile indicator by RunStrat (RS: Market Profile), equipped with features such as marking the Point of Control (POC), calculating the Value Area, and highlighting the Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP).
For those interested in exploring Market Profile and Volume Profile on TradingView, we have great news! New users can usually access a 30-day free trial of TradingView’s premium features using our link. Additionally, you can receive a discount on your subscription, providing even more value for your trading journey.
Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting, utilizing Market Profile and Volume Profile on TradingView can be a valuable addition to your trading toolkit, unlocking insights into market behavior and potential opportunities.
Exclusive Deal: 30-Day FREE Premium Access + Bonus Credit
Don’t Miss Out – Sign up for TradingView Now!
- Advanced Charts
- Real-Time Data
- Track all Markets
FAQ
Who created auction market theory?
Pete Steidlmayer developed the auction market theory in the 1980s. Jim Dalton is also known for being the godfather of the market profile and auction market theory.
What is an auction market in simple terms?
An auction market is a market where buyers and sellers compete by placing bids and offers for a certain item or asset. The price of the item or asset is determined by the interaction of supply and demand, as well as the rules of the auction. An example of an auction market is the stock exchange, where traders buy and sell shares of companies.
What is the value area of the auction market theory?
The value area of the auction market theory is the range of prices where most of the trading activity occurs. It represents the fair price or equilibrium price of the item or asset, where buyers and sellers agree on its value. The value area can be identified by using tools such as market profile or volume profile, which show the distribution of volume or time at different price levels.
What are examples of auction theory?
Auction theory can be applied to various situations where resources are allocated through bidding mechanisms. Some examples of auction theory are:
- Spectrum auctions, where governments sell licenses to use radio frequencies for telecommunications services.
- Treasury auctions, where governments sell bonds or bills to finance their budget deficits.
- Art auctions, where collectors bid for paintings or sculptures by famous artists.
- Charity auctions are where donors bid for items or experiences to raise money for a cause.
- Online auctions, where buyers and sellers trade goods or services on platforms such as eBay or Amazon.
How do you trade auction market theory?
To trade auction market theory, you need to understand the dynamics of order flow and price action in an auction market. You need to identify the balance and imbalance phases of the market, as well as the initiating and responsive activities of buyers and sellers. You also need to recognize the acceptance and failed auction scenarios, which indicate whether the market has found a new value area or rejected a price level. You can use tools such as market profile or volume profile to visualize the structure and behavior of the market.
What are the different types of auction game theory?
Auction game theory is a branch of game theory that studies how bidders strategize and interact in different types of auctions. Some common types of auctions are:
- First-price sealed-bid auctions, where bidders submit their bids secretly and the highest bidder wins and pays their bid.
- Second-price sealed-bid auctions, also known as Vickrey auctions, where bidders submit their bids secretly and the highest bidder wins but pays the second-highest bid.
- English auctions, also known as open ascending price auctions, where bidders openly raise their bids until no one is willing to bid higher.
- Dutch auctions, also known as open descending price auctions, where the seller starts with a high price and lowers it until a bidder accepts it.
- All-pay auctions, where bidders pay their bids regardless of whether they win or not.
What is auction theory what are its applications?
Auction theory is an applied branch of economics that deals with how bidders act in auction markets and how the features of auction markets incentivize predictable outcomes. Auction theory is a tool used to inform the design of real-world auctions. Some applications of auction theory are:
- Designing efficient and fair mechanisms for allocating scarce resources such as spectrum licenses, electricity contracts, carbon permits, etc.
- Evaluating the performance and revenue potential of different auction formats and rules.
- Analyzing the strategic behavior and incentives of bidders and sellers in various auction settings.
- Developing bidding strategies and algorithms for participating in complex auctions.
What is TPO auction theory?
TPO stands for time-price opportunity, which is a way of measuring how much time the market spends at a certain price level. TPO auction theory is based on using market profile, which is a graphical tool that shows the distribution of TPOs across different price levels. TPO auction theory helps traders understand how the market values an item or asset over time, and how it transitions from one value area to another.
– Free trading journal template & cheat sheet PDFs
– Access our custom scanners and watchlists
– Access our free trading course and community!