IVV vs. VUG – Which is Best For You?
Discover my comparison of IVV vs. VUG to determine which is best for you. I have compiled all of the information about these funds across the internet in this article to make your research easier.
IVV vs. VUG Key Characteristics
You can use the table below to compare the key characteristics of these funds:
| Metrics | IVV | VUG |
|---|---|---|
| 1-Year Annual Return | 26.27% | 46.78% |
| 5-Year Annual Return | 15.65% | 19.17% |
| Expense Ratio | 0.03% | 0.04% |
| Dividend Yield | 1.45% | 0.52% |
| Number of Holdings | 508 | 221 |
You can compare these funds in real time using the TradingView chart below. Ensure to click the “ADJ” button at the bottom right of the chart to adjust the data for dividends! While TradingView doesn’t support mutual funds, you can change them to the ETF equivalent to see the returns in real-time.
Overview of IVV
The iShares Core S&P 500 ETF, known by its ticker symbol IVV, is an exchange-traded fund managed by BlackRock. This ETF is designed to track the performance of the S&P 500 Index, which comprises 500 of the most established and financially robust companies in the United States, spanning multiple industries.
Overview of VUG
The Vanguard Growth ETF, VUG, is an exchange-traded fund managed by Vanguard. VUG is specifically designed to track the performance of the CRSP US Large Cap Growth Index, which comprises large U.S. companies exhibiting growth characteristics. While VUG offers exposure to growth segments of the large-cap market, this focus also entails specific risks associated with growth investing, such as higher price volatility and sensitivity to market cycles.
Performance Comparison of IVV vs. VUG
The total return performance including dividends is crucial to consider when analyzing different investment funds.
As of 1/15/2024, IVV has a one year annualized return of 26.27%, while VUG has a five year annualized return of 46.78%.
IVV vs. VUG Dividend Yield
Both IVV and VUG pay dividends to their shareholders from the earnings of their underlying stocks. The dividend yield is a measure of how much a company pays in dividends relative to its share price.
As of 1/15/2024 the dividend yield of IVV is 1.45%, while the dividend yield of VUG is 0.52%.
IVV vs. VUG Expense Ratios
The expense ratio is a measure of how much an ETF charges its investors for managing the fund. It is expressed as a percentage of the fund’s assets per year.
The expense ratio is one of the most important factors to consider when choosing an ETF because it directly affects your returns over time. The lower the expense ratio, the more money you get to keep from your investment.
As of 1/15/2024 IVV has an expense ratio of 0.03%, while VUG has an expense ratio of 0.04%.
IVV vs. VUG Holdings
A fund’s holdings are the basket of individual securities that it owns and tracks. It is crucial for investors to analyze a fund’s holdings because they are effectively what you are investing in by purchasing the fund.
As of 1/15/2024 IVV holds 508 securities, while VUG holds 221.
Mutual Funds vs. ETFs
When comparing investment funds, you may be confused about the difference between an ETF and a mutual fund. Keep in mind, an index fund is a specific type of mutual fund. ETFs are tradeable during the stock market hours, while mutual funds only update once per day.
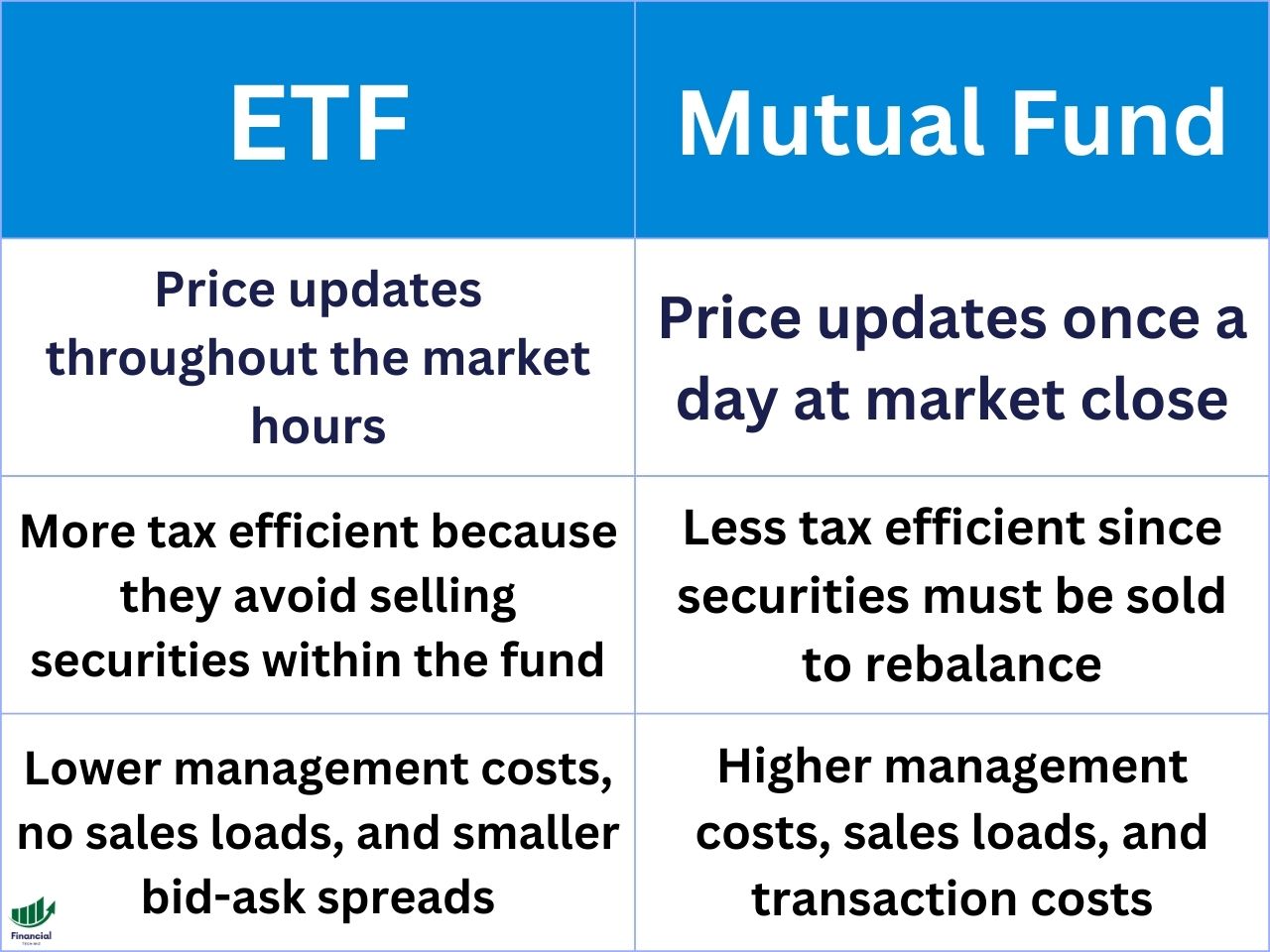
Mutual funds are pooled investment vehicles that are managed by a fund company or an investment advisor. They issue and redeem shares directly to investors at the end of each trading day based on their net asset value (NAV). Investors can buy and sell mutual fund shares through the fund company or a broker.
ETFs are also pooled investment vehicles that are managed by a fund company or an investment advisor. However, they trade like stocks on an exchange throughout the trading day at market prices that may differ from their NAV. Investors can buy and sell ETF shares through a broker.
Some of the advantages and disadvantages of mutual funds vs ETFs are:
- Mutual funds may offer more convenience and flexibility for investors who want to invest a fixed amount of money or set up automatic investments or withdrawals.
- Mutual funds may require a larger minimum investment.
- ETFs may incur bid-ask spreads and premiums or discounts to their NAV, which can affect their trading efficiency and performance.
- Mutual funds may be less tax-efficient than ETFs, as they may distribute more capital gains to their shareholders due to their redemption mechanism.
- ETFs may be more tax-efficient than mutual funds, as they may avoid realizing capital gains through their creation and redemption mechanism.
IVV vs. VUG – Bottom Line
Ultimately, both IVV and VUG are solid investment choices. The choice between the two ultimately depends on the exposure you want and the amount of risk you are willing to take.
Hopefully, the information in this article helps you decide which is better for your portfolio. To continue your research, check out our other fund comparison articles as well!
Comparing ETFs With TradingView
When comparing ETFs, it is crucial that you are comparing the total return to include dividend payments. TradingView allows you to compare several stocks and ETFs at once on a single chart adjusted for dividends.
You can simply sign up for a free TradingView account and type the stock ticker you want to compare.
Exclusive Deal: 30-Day FREE Premium Access + Bonus Credit
Don’t Miss Out – Sign up for TradingView Now!
- Advanced Charts
- Real-Time Data
- Track all Markets
Next, click the plus sign next to the ticker at the top left of the chart to add symbols to compare.
Finally, ensure you click the ‘ADJ’ at the bottom to adjust the returns for dividends!
TradingView is the best way to compare multiple funds and ETFs on a single chart, making your research much easier. Feel free to compare any ETFs you’d like using the widget at the top of this page. Alternatively, sign up for a free TradingView account and use the main website for a better experience. You can also watch the video below to learn how to compare funds with TradingView:
Other ETF Comparisons
– Free trading journal template & cheat sheet PDFs
– Access our custom scanners and watchlists
– Access our free trading course and community!